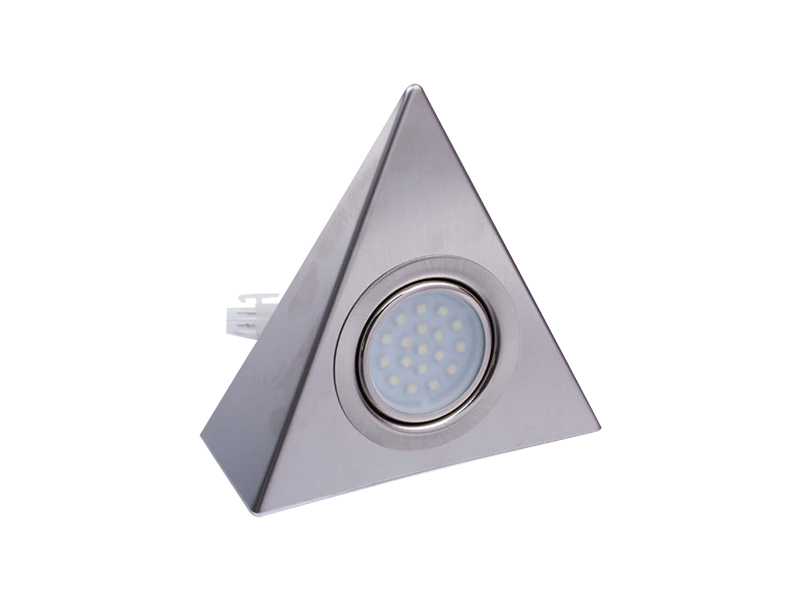
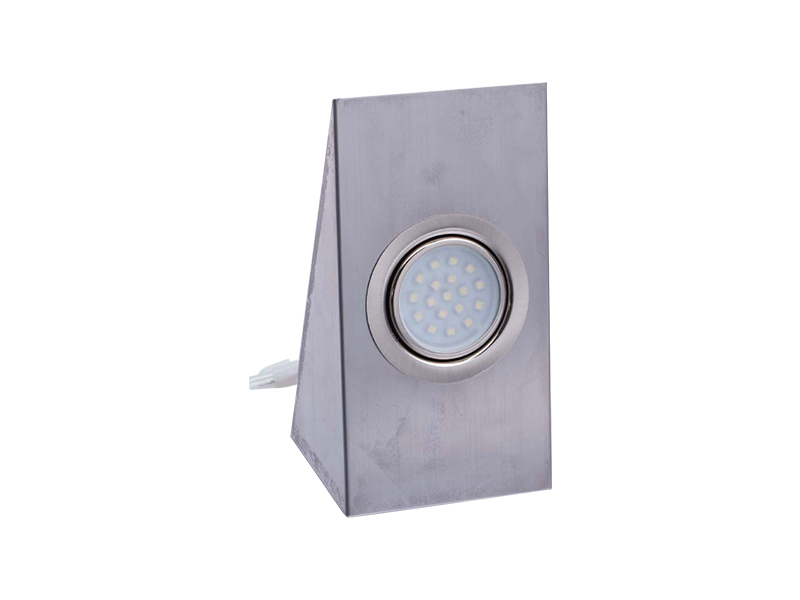
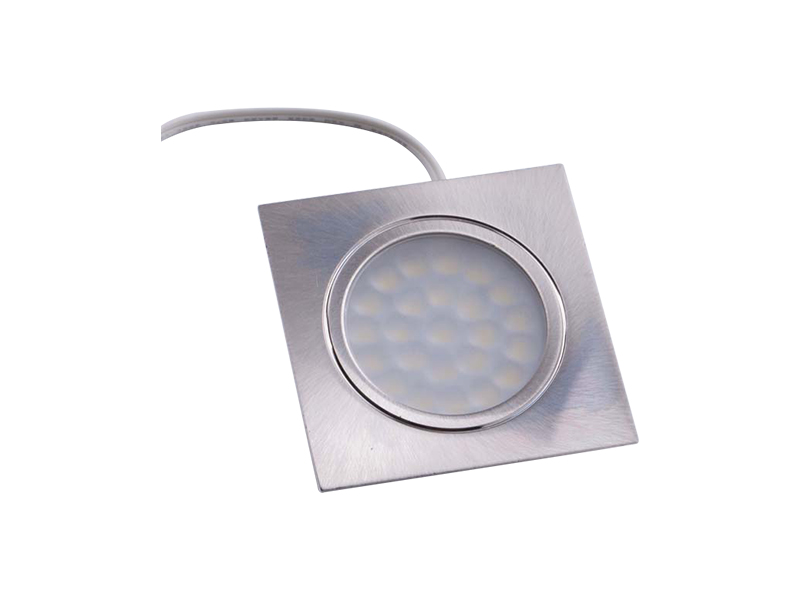
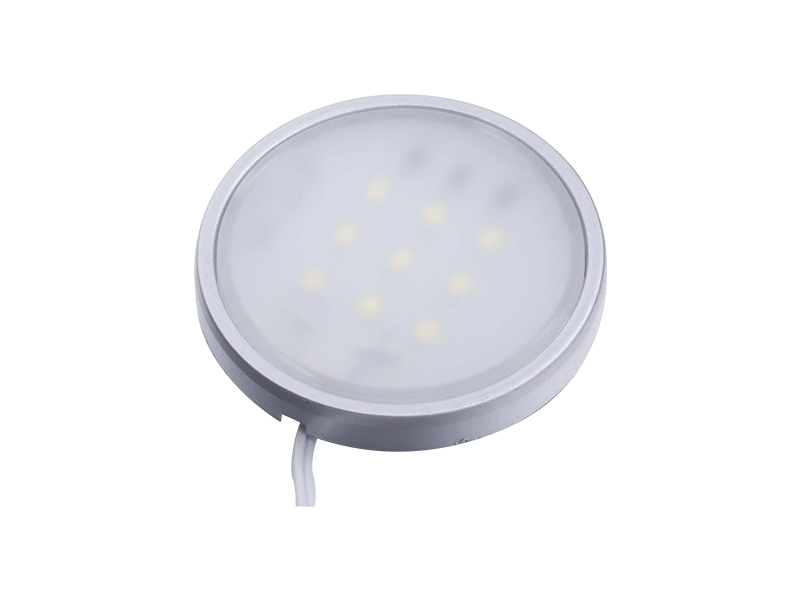
-
E-mail:[email protected]
-

Telphone:+86-574-88073028
-

FAX:+86-574-88073029
QR code on
mobile phone
Welcome to Eastkey!
Welcome to Dongke!
The heat dissipation design of LED Front Mirror Light is one of the key factors to ensure the efficient and stable operation of LED lamps. Since LED lamps generate a lot of heat during operation, a reasonable heat dissipation design can not only increase the service life of the lamps, but also improve their performance and reliability. The heat dissipation design of LED front mirror lights will be discussed in detail below, including heat dissipation principles, main heat dissipation technologies, selection of heat dissipation materials and design considerations.
1. Heat dissipation principle
When working, LED lamps convert electrical energy into light energy, but also generate heat. The operating temperature of LED chips directly affects their brightness, color temperature and service life. If the temperature is too high, the performance of LED chips will decline or even burn out. Therefore, the main goal of heat dissipation design is to effectively guide the heat generated by LED lamps out of the lamps and keep the LED chips within a stable operating temperature range.
2. Main heat dissipation technology
In order to effectively manage the heat of LED front mirror lights, common heat dissipation technologies include the following:
Heat sink: The heat sink is the core component in the heat dissipation design of LED lamps. Usually made of highly thermally conductive materials such as aluminum or copper, heat sinks increase the efficiency of heat dissipation by increasing the surface area in contact with the air. Heat sinks can be designed in a variety of shapes, such as fins, sheets, or columns, to enhance air circulation and heat conduction.
Heat pipe: A heat pipe is an efficient heat conduction device that can quickly conduct heat from the LED chip to the heat sink. The heat pipe contains a liquid inside, which evaporates when heated and moves to the cold end of the heat pipe, and then condenses into a liquid, forming a cycle process to take away the heat.
Thermal interface material: Thermal interface material (TIM) is used to improve the efficiency of heat conduction between the LED chip and the heat sink. Commonly used thermal interface materials include thermal paste, thermal pads, and thermal adhesives, which fill the tiny gaps between the chip and the heat sink to ensure better heat transfer.
Active air cooling: Some high-power LED lamps may be equipped with fans or other active cooling systems to enhance the heat dissipation effect. The fan removes heat by forced air flow, thereby reducing the operating temperature of the LED lamp.
3. Selection of heat dissipation materials
Choosing the right heat dissipation material is crucial for the heat dissipation effect of LED front mirror lights.
Aluminum alloy: Aluminum alloy is often used as a heat sink material for LED lamps due to its good thermal conductivity and lightweight properties. Aluminum alloy not only conducts heat effectively, but also has good corrosion resistance and processability.
Copper: Copper has higher thermal conductivity, but it is more expensive and heavier than aluminum. In some high-power LED lamps, copper is used in key heat dissipation areas to improve heat dissipation efficiency.
Thermal conductive silicone: Thermal conductive silicone is a commonly used thermal interface material with good thermal conductivity and flexibility. It can effectively fill the tiny gap between the LED chip and the heat sink to ensure effective heat transfer.
4. Design considerations
When designing the heat dissipation system of LED front mirror lights, the following factors need to be considered:
Power density: The power density (i.e., power per unit area) of the LED lamp affects the complexity of the heat dissipation design. The higher the power density, the more heat is generated and the higher the requirements for the heat dissipation system.
Environmental conditions: The use environment of the LED lamp has an impact on the heat dissipation design. For example, when using LED lamps in high temperature environments or enclosed spaces, special considerations need to be given to the heat dissipation design to avoid overheating problems.
Heat dissipation path: When designing a heat dissipation system, the heat transfer path needs to be considered. Ensure that the heat can be effectively transferred from the LED chip to the heat sink and finally dissipated into the air.
Structural design: The structural design of the LED front mirror lamp will also affect the heat dissipation effect. For example, the housing design of the lamp needs to leave enough heat dissipation space and ensure good air circulation.
top
E-mail:[email protected]
Telphone:+86-574-88073028
FAX:+86-574-88073029





